Section 5 Pathway crosstalk
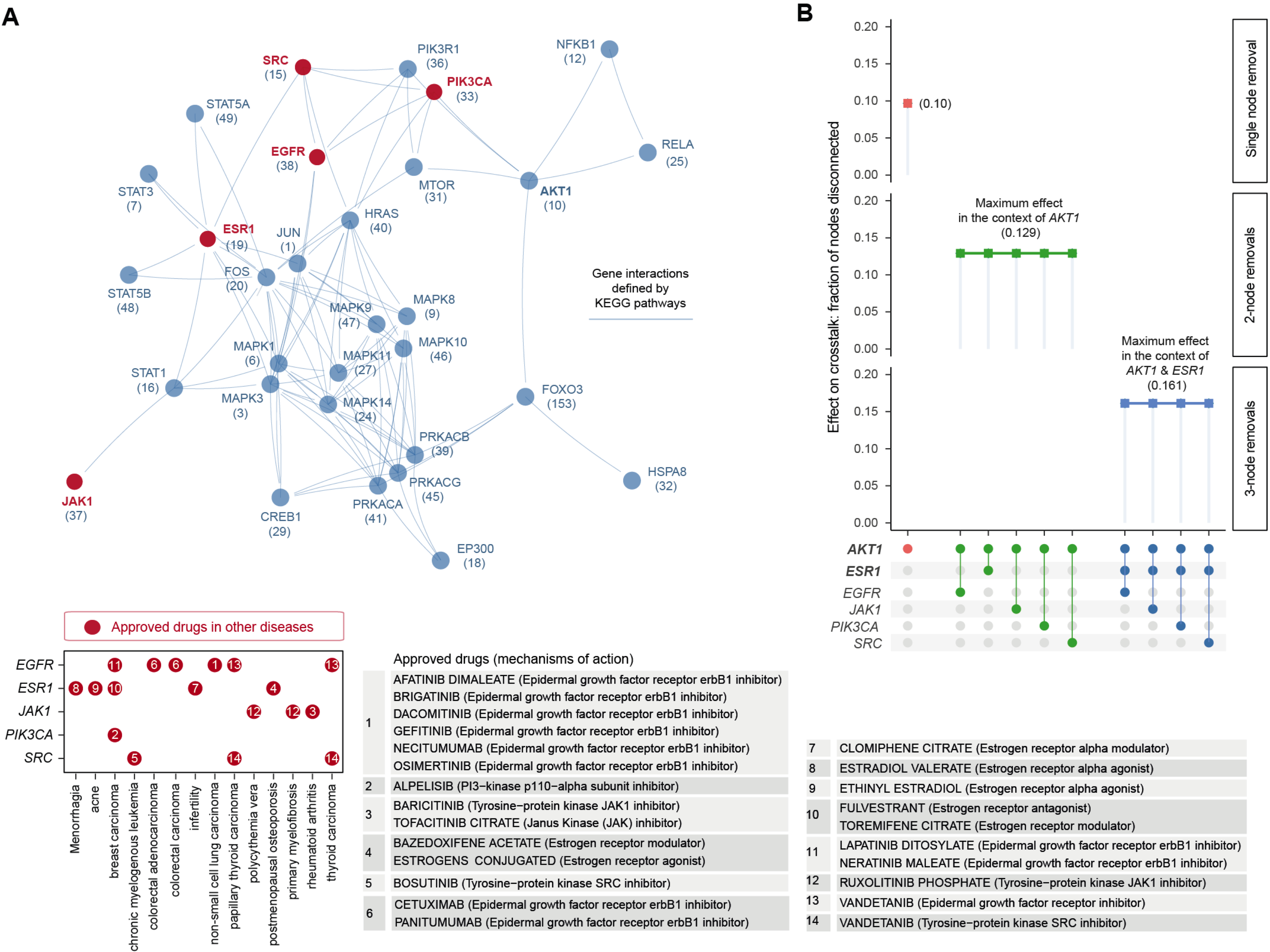
Figure 5.1: Pathway crosstalk-based attack analysis identifies critical genes and repurposes licensed medications. (A) Pathway crosstalk identified by integrating target prioritisation information with knowledge of gene interactions. Nodes are labelled by gene symbols together with priority rank. Crosstalk genes that are currently targeted by approved drugs in other disease indications are highlighted in red. These approved drug target genes (y-axis) and disease indications (x-axis) are detailed beneath, with dots indexed in number and referenced on the right panel showing information on drugs and mechanisms of action. (B) Effect of node removals on the crosstalk. Top: the single-node effect maximised by removing ATK1, the maximum effect of removing an additional approved drug target in the context of AKT1, and the maximum effect of removing an additional approved drug target in the context of AKT1 and ESR1. Bottom: node removals are indicated by colored circles.